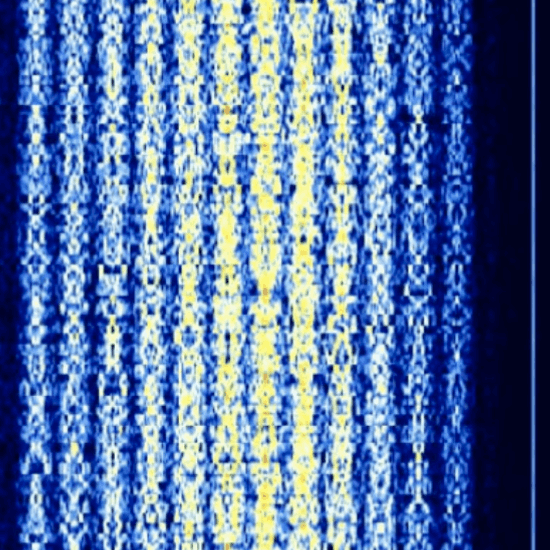
CIS 12
CIS 12
- Digital modem (RUS).
- Encrypted data and voice.
- Bandwidth 2.6 kHz.
- Easy to determine in the waterfall.
- 12 digital channels and a pilot tone on 3.3 kHz.
- Pilot tone clearly recognisable on the right edge of the screenshot.
The following examples show the most important intruders that we encounter in the exclusive amateur radio shortwave bands. The screenshots have been selected so that they come as close as possible to the appearance with amateur radio equipment.

CIS 12
- Digital modem (RUS).
- Encrypted data and voice.
- Bandwidth 2.6 kHz.
- Easy to determine in the waterfall.
- 12 digital channels and a pilot tone on 3.3 kHz.
- Pilot tone clearly recognisable on the right edge of the screenshot.
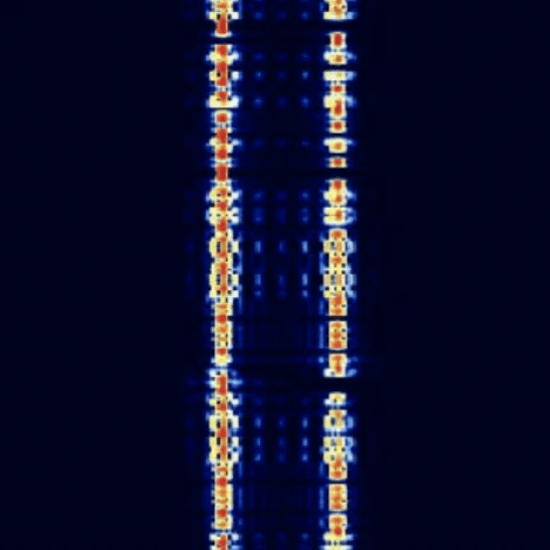
CIS 36-50 50-50
- Digital FSK modem of the Russian Navy.
- Hardly distinguishable from an amateur radio RTTY signal at first glance.
- Characteristic: Shift often 250 Hz, also e.g. 200 Hz or 500 Hz.
- Variable, often 50 baud.
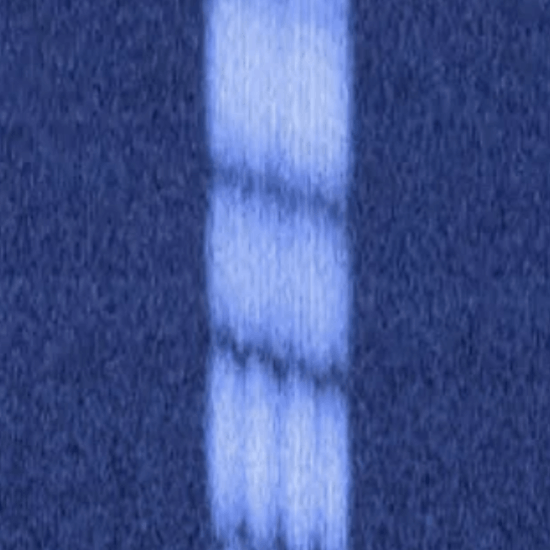
STANAG 4285
- NATO digital PSK modem for data and voice.
- Characteristic veil in the waterfall of around 3 kHz width.
- 2400 baud.
- BPSK, QPSK, 8-PSK.
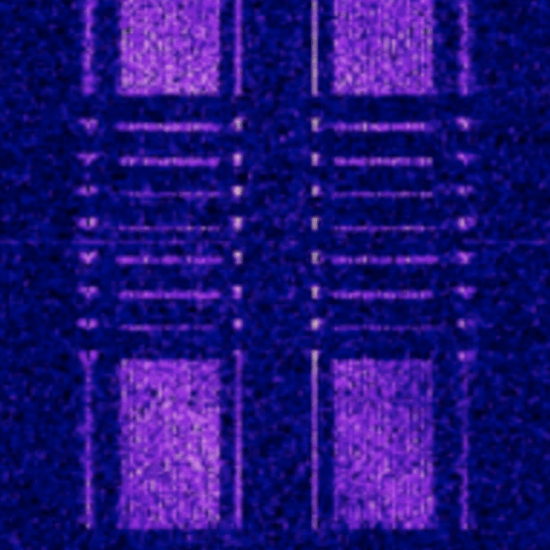
LINK-11
- NATO digital modem.
- Tactical data, mostly naval.
- CLEW mode 2.31 kHz bandwidth.
- SLEW mode 3.00 kHz bandwidth.
- 1 or 2 characteristic data streams in waterfall.
- DQPSK, PSK.
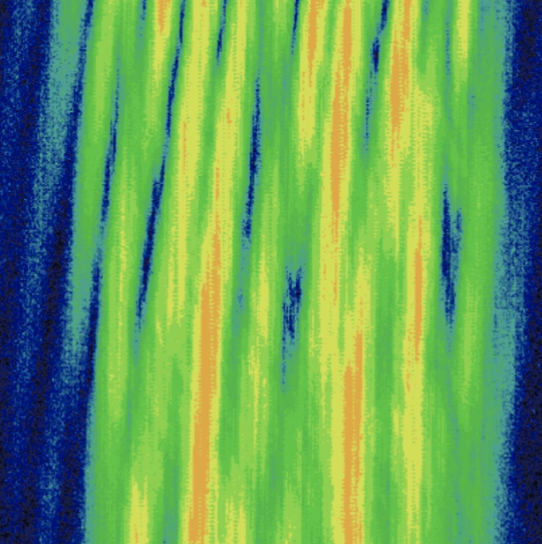
OTHR
- Veil-like, broad strip in the waterfall.
- Bandwidths mostly between 10 - 160 kHz.
- Acoustic impression. Humming sound or alternating sound.
- Mostly caused by RUS, CHN, IRN or NATO.